IRAS Explanatory Supplement
V. Data Reduction
D. Point Source Confirmation
D.2 Overview of Seconds-Confirmation
D.2.e Double-Detection Mode
Table of Contents | Index | Previous Section | Next Section
The double-detection mode was the most common mode of seconds-confirmation. A combined test on flux and position was applied which consisted of a two-degree-of-freedom
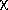 2 test.
The n-
2 test.
The n- position discrepancy
contributed one of the degrees of freedom, and the discrepancy
in the log of the two fluxes in units of the log-flux standard
deviation provided the other. A threshold value corresponding
to sacrificing one real event out of every hundred thousand was
used for this test for unconfused cases, and one corresponding
to sacrificing one real source in a million was used for cases
which had been processed for confusion before arriving at this
point. If this test failed, the drop-dead fell back to rejection
processing as described above; otherwise parameter refinement
was performed for the flux and position (see below), and the next
detection was processed.
position discrepancy
contributed one of the degrees of freedom, and the discrepancy
in the log of the two fluxes in units of the log-flux standard
deviation provided the other. A threshold value corresponding
to sacrificing one real event out of every hundred thousand was
used for this test for unconfused cases, and one corresponding
to sacrificing one real source in a million was used for cases
which had been processed for confusion before arriving at this
point. If this test failed, the drop-dead fell back to rejection
processing as described above; otherwise parameter refinement
was performed for the flux and position (see below), and the next
detection was processed.
Table of Contents | Index | Previous Section | Next Section